Truebit Protocol Attack Analysis: 8,535 ETH Lost to Integer Overflow
A detailed vulnerability analysis of the Truebit Protocol exploit on January 8, 2026, where an attacker exploited an integer overflow vulnerability in the token purchase price calculation logic, resulting in a loss of 8,535.36 ETH.
ExVul Security Team
Security Research
On January 8, 2026, the Truebit Protocol was compromised by a hacking attack, resulting in a loss of 8,535.36 ETH. The official team of Truebit Protocol issued a statement in the early hours of the following day to confirm the incident. The ExVul Security Team has conducted a detailed vulnerability analysis of this attack, and the findings are as follows.
Attack Flow
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Attacker Address | 0x6c8ec8f14be7c01672d31cfa5f2cefeab2562b50 |
| Attack Transaction Hash | 0xcd4755645595094a8ab984d0db7e3b4aabde72a5c87c4f176a030629c47fb014 |
The attacker completed the exploit by invoking a cycle of transactions in the sequence of getPurchasePrice → 0xa0296215 → 0xc471b10b for 4 iterations. An analysis based on the first iteration is provided below.
Step 1: The attacker first called the function getPurchasePrice(240442509453545333947284131), which returned a value of 0.
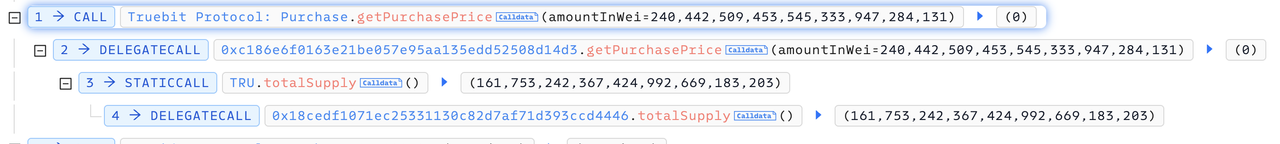
Step 2: The attacker invoked the function 0xa0296215(c6e3ae8e2cbab1298abaa3) with msg.value set to 0, and succeeded in minting 240442509453545333947284131 TRU tokens.
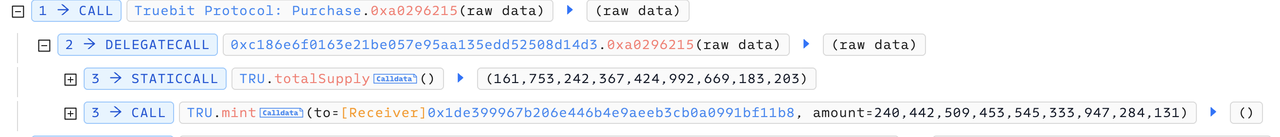
Step 3: The attacker invoked the function 0xc471b10b(c6e3ae8e2cbab1298abaa3), and burned 240442509453545333947284131 TRU tokens to obtain 5105.06 ETH.
Analysis of the Attack Logic
By examining the aforementioned attack flow, it can be clearly identified that there are flaws in the logic of the getPurchasePrice function and the 0xa0296215 function. An in-depth analysis is provided below (note: as the contract is not open-source, all the code cited hereinafter is decompiled code).
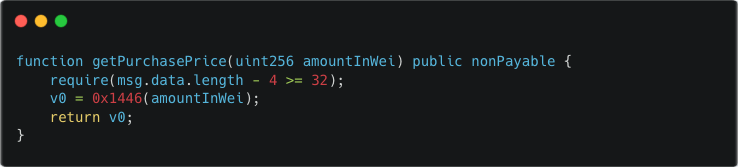
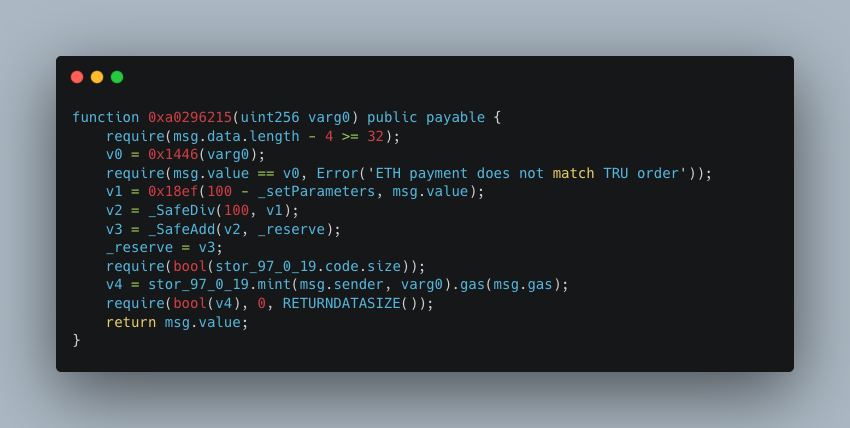
By comparing the commonalities of the two functions, we can see that the 0x1446 function is designed to calculate the amount of ETH required to purchase a specified quantity of TRU tokens. It is evident that flaws exist in the logic of the 0x1446 function, which results in incorrect ETH calculation. A detailed analysis of the logic within the 0x1446 function is provided below.
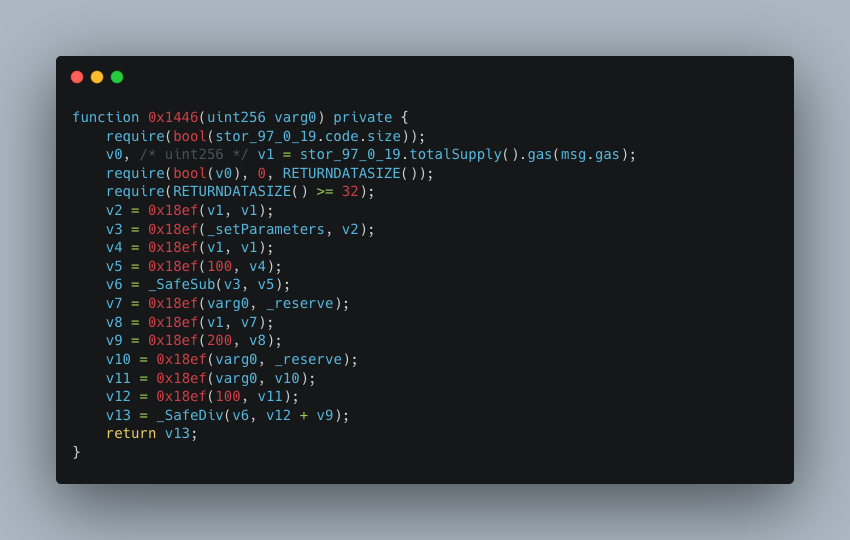
Observing the logic within the 0x1446 function, since the final calculation result v13 == 0, there must be flaws in the aforementioned calculation logic. It is important to note that the functionality of 0x18ef is identical to that of _SafeMul; therefore, the issue lies in the use of the native addition operation v12 + v9 (the contract version is ^0.6.10, which does not include overflow checks).
v12 and v9 represent:
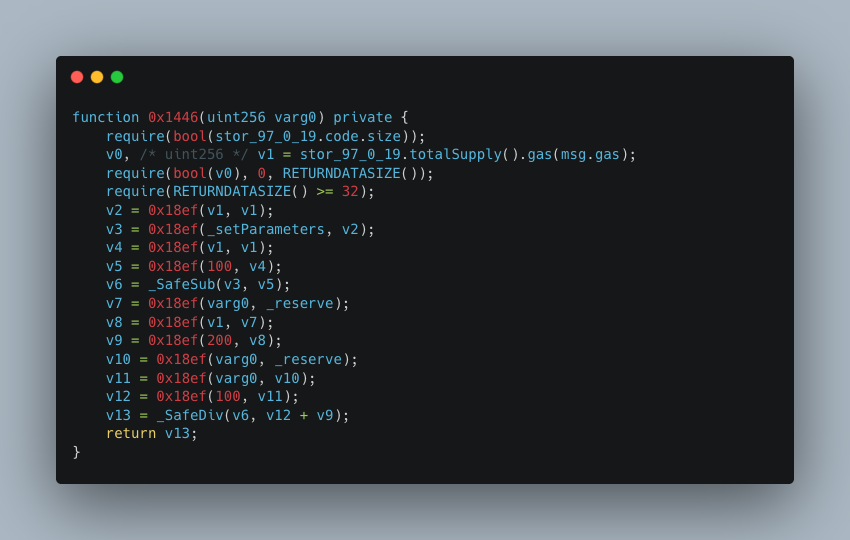
Based on the above analysis, the attacker's exploit approach was to input an extremely large _amountIn value, which caused the arithmetic operation v12 + v9 to overflow into an extremely small value. Ultimately, this resulted in the calculation (v12 + v9) / v6 == 0.
Summary
The fundamental cause of the Truebit Protocol exploit was a severe integer overflow vulnerability in its token purchase price calculation logic. Because the contract used Solidity version 0.6.10 and lacked safety checks for critical arithmetic operations, it resulted in a significant loss of 8,535.36 ETH.
While newer versions of Solidity (0.8.0 and above) have built-in protections to mitigate overflow vulnerabilities, this incident highlights a growing trend. This attack appears to be the work of hackers using AI automation to scan established, legacy DeFi protocols for unpatched vulnerabilities—similar to the recent attacks on Balancer and yETH.
We anticipate that AI-driven attacks targeting older DeFi protocols will continue to increase in the near future.
Recommendations
Conduct Fresh Security Audits
Review existing contract code with modern security tools and methodologies to identify legacy vulnerabilities.
Upgrade or Migrate
Upgrade contracts or migrate assets immediately if vulnerabilities are discovered in legacy code.
Implement On-Chain Monitoring
Deploy robust on-chain monitoring to detect anomalies in real-time and minimize potential losses.